
There is much confusion about the term (and location) called the metaverse. Most of us know that the term is credited to author Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash. The next perspective came from the book Ready Player One by Ernest Cline, its diversity further explored in the sequel, Ready Player Two. But what is it really?
Dictionaries define the metaverse as:
A virtual-reality space in which users can interact with a computer-generated environment and other users.
That is the core, but it is so much more. A more recent AI generated definition is:
A collective virtual shared space created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and persistent virtual environments. It encompasses all virtual worlds, augmented reality, and the internet. The concept suggests an immersive version of the internet where users can interact, learn, work, shop, and play through avatars in a 3D environment.
Both of these definitions assume that the metaverse is a virtual space, yet it isn’t. It is all around us. As the technology speeds along its evolutionary path, we are moving closer and closer to the Star Trek Holodeck experience.
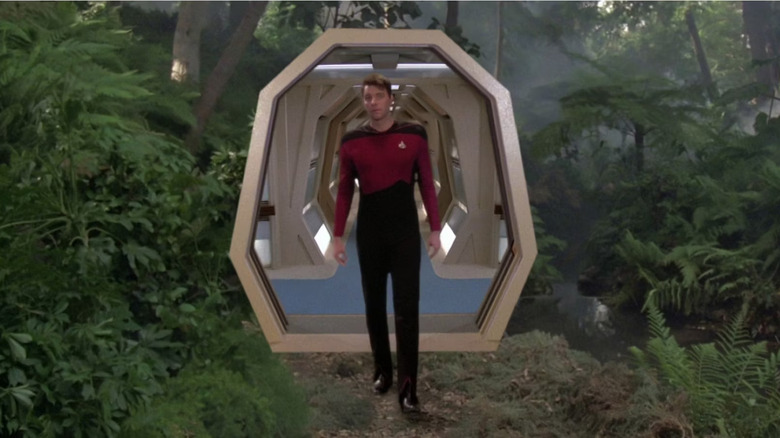

The holodeck was introduced to the Star Trek culture in 1973 after Star Trek creator Gene Roddenberry met Gene Dolgoff, owner and developers of a holography lab in New York City. The realistic 3D simulation inspired Roddenberry to feature a holodeck-like technology in the Star Trek: The Animated Series, and later in Star Trek: The Next Generation where it continued to be used in many story lines across the different series. In Star Trek: Discovery, the holodeck as well as mixed reality and augmented reality elements are integrated right into the ship.
It is the latter that defines our future with the metaverse where the line between virtual and reality is merged and integrated into our lives.

It is already happening with virtual displays seen through AR glasses that are interactible, allowing us to control simple tasks that will soon become full computer and AI-driven programs.
Thus, the metaverse is all around us. At least it will be soon.
Remember, the terms metaverse, virtual reality, eXtended reality, spatial computing, and so on are just the start of the language that will evolve from these pioneering days of VR headsets and AR glasses in virtual worlds and experiences.
Where is the Metaverse Today?
We’ve peeked at the past and future, but where is the metaverse today?
For over 25 years, the metaverse’s original definition of a computer-generated environment with multi-user collaboration has been in Second Life as a 2D experience through a computer. In 2015, the first consumer VR headsets hit the market. Social VR left the 2D space to become 3D with VR platforms such as AltspaceVR, vTime, Rec Room, and VRChat rose up to represent the social, multi-player experience of the metaverse.
Augmented reality (AR) and the earliest mixed reality (MR) experiences reached enterprise and consumer customers about 2013 with Google Glass, followed by the Microsoft HoloLens. AR and MR arrived on our smartphones a year earlier in 2012 with the global release of Ingress by Niantic (Google), later to be revamped and called Ingress Prime. Ingress continues today on its own as well as the underlying code platform for Pokemon Go, Wizards Unite (Harry Potter), Pikmin Bloom, Catalan, and the latest, Monster Hunter Now.
The interactive and collaborative nature of the Niantic Ingress-based games use geolocation over a virtual or mixed reality playing field. Guided to key landmarks, players interact with other characters or elements in the game as they play. They work in teams with others, often the enemy, to capture land and creatures to increase their score.
With the release of AR glasses to consumers at a more affordable price, more and more people are using their phones as hot spots to power the virtual experience through their lenses. AR technology developed through programs like Niantic now aid shoppers to find their way through grocery and big box stores and in and around cities using directional arrows and map overlaps.
We used to have 2D images for our social media profile pictures. Today, some social media platforms are embracing 3D avatars that represent individuals not only on their social media pages but across XR virtual environments.
These are just the first steps in exploring and exploiting the virtual metaverse. With the integration of artificial intelligence, the metaverse will evolve even faster.
The Metaverse in Education and Careers
The current estimates about the global XR market fluctuates every year. In 2023, estimates are that the current market is valued at $57 Billion USD. By 2024, it is estimated to reach $160 Billion.
Generative AI, artificial intelligence that can create original content from images to video to 3D physical and virtual objects, will be valued at $2.5 trillion by 2030.
These numbers are speculative and come from a variety of sources representing the commitment industry and science have in the virtual future and integration into our lives.

Second Life was embraced by colleges and universities soon after it launched in 2003. Some of the top universities still have worlds and classes in there. These and many schools around the world for all ages have expanded onto social VR platforms including ENGAGE XR, Spatial.io, Frame VR, and VRChat, to name just a few.
It is likely that you may have even used a VR headset in one of your classes? It is used to teach history, host virtual field trips, train medical and emergency students, language learning, and even career opportunity and training experiences.
The medical and healthcare industry has been using VR for not just staff training and education but therapy including mental healthy, physical, and stress reduction.

Auto manufacturers and dealers are using VR to introduce new vehicles and train buyers on how to use them.
Farmers are using a mix of AR and MR on everything from their phones and tablets to modern machine equipment to evaluate the plants, soil conditions, micro climates, weeds, and even the status and instructions for vehicle maintenance.
NASA and other daring space-faring companies are using XR to not just train astronauts but create simulations of life on the spacecraft and a new planet. NASA recently announced the NASA Human Exploration Rover Challenge to creates a vehicle for traveling on other planets through the rough and unforgiving terrain using VR technology.
As schools rise to meet the demand for XR technology jobs in:
- VR/AR development
- 3D modeling and animation
- Blockchain and virtual engineering
- UI/UX design for virtual environments
- Data analysis and AI for personalized experiences
- Cybersecurity for virtual worlds
- Content creation for immersive media
- Virtual event planning and management
These aren’t skills needed just in the future. They are skills needed now by companies that have a high demand for metaverse-related skills:
- Information Technology (IT)
- Leading investor in metaverse technology
- Developing foundational platforms and tools
- Medical and healthcare
- Educational training including nursing and surgeries
- Digital twin assets, environments, and experiences (simulations)
- Experimentation and research
- Mental and physical health therapies
- Emergency response and preparedness training
- Entertainment and Media
- Virtual concerts and events
- Interactive storytelling and content creation
- Creating immersive gaming experiences
- Gaming includes educational applications as well as entertainment
- Developing digital assets and blockchain-based games assets
- Real Estate
- Virtual property development and sales
- Creating digital twins of physical properties
- Retail
- Virtual shopping experiences
- Product development and displays
- Digital product showcases and demos
- Financial Services
- Virtual banking and financial transactions
- Blockchain and cryptocurrency integration
- Manufacturing
- Virtual product design and prototyping
- Testing and experimenting
- Training and maintenance simulations
- Marketing and Advertising
- Immersive brand experiences
- Virtual influencer marketing
How is Girls STEAM InstituteTM Meeting the Demand?

In 2021, Girls STEAM Institute (GSI) launched their first virtual reality business challenge during the COVID pandemic. High school age girls came from around the world to participate in teams to solve world problems.
Diane McClelland, CEO, realized that virtual reality would be a powerful influence on future careers. She partnered with Educators in VR and the Virtual World Society to make that bold step to bring her alumni and new members into the future together.
Each year, GSI’s participation into virtual reality has expanded. They meet regular in ENGAGE XR, a professional social VR platform, with experts in emerging technology and career development. In 2024, they offered their first Girls STEAM Institute Business Challenge for parents, mentors, and teachers to encourage them to support young women in emerging technology.
The effort continues today. To find out how you can take the next step into emerging technology and become involved with Girls STEAM Institute as a participant, parent, mentor, partner, or sponsor, check out our GSI Join page or join us at one of our many online events.
The metaverse, whatever it will be called, is here today and will be integrated into our lives in the future. So join us as we explore the next frontier together.



